
Canada, known for its leading hydrogen and fuel cell technology companies, is also well positioned to attract direct foreign investment and continue to grow as a word-leading exporter of technology, products, and services. Canada has the potential to produce large amounts of low-cost, clean hydrogen in excess of its domestic demand, creating an opportunity for Canada to become a supplier of choice of a new carbon-free energy export commodity. Momentum for hydrogen and fuel cell technology is growing globally, with the global market value expected to reach as much as $11.7 trillion by 2050. To diversify our future energy mix, generate economic benefits, and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, Canada must work to make a clean hydrogen economy a strategic priority. The need to mitigate climate change is transforming energy systems around the world, and hydrogen has a critical role to play in the creation of a carbon-neutral future. Gravimetric energy density: highest energy per mass of any fuel The power to reach net-zero Volumetric energy density: low volumetric density requires advanced storage methodsĭetectability: invisible, odourless and tastelessĪbundancy: 75% of the mass of the universe
Mass of a hydrogen atom free#
Natural state: rarely exists in a free stateĮnergy carrier: stores energy first created elsewhere If I take the hydrogen atom, and try to predict its mass this way. Weights of atoms and isotopes are from NIST article. (1 u is equal to 1/12 the mass of one atom of carbon-12) Molar mass (molar weight) is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in g/mol.
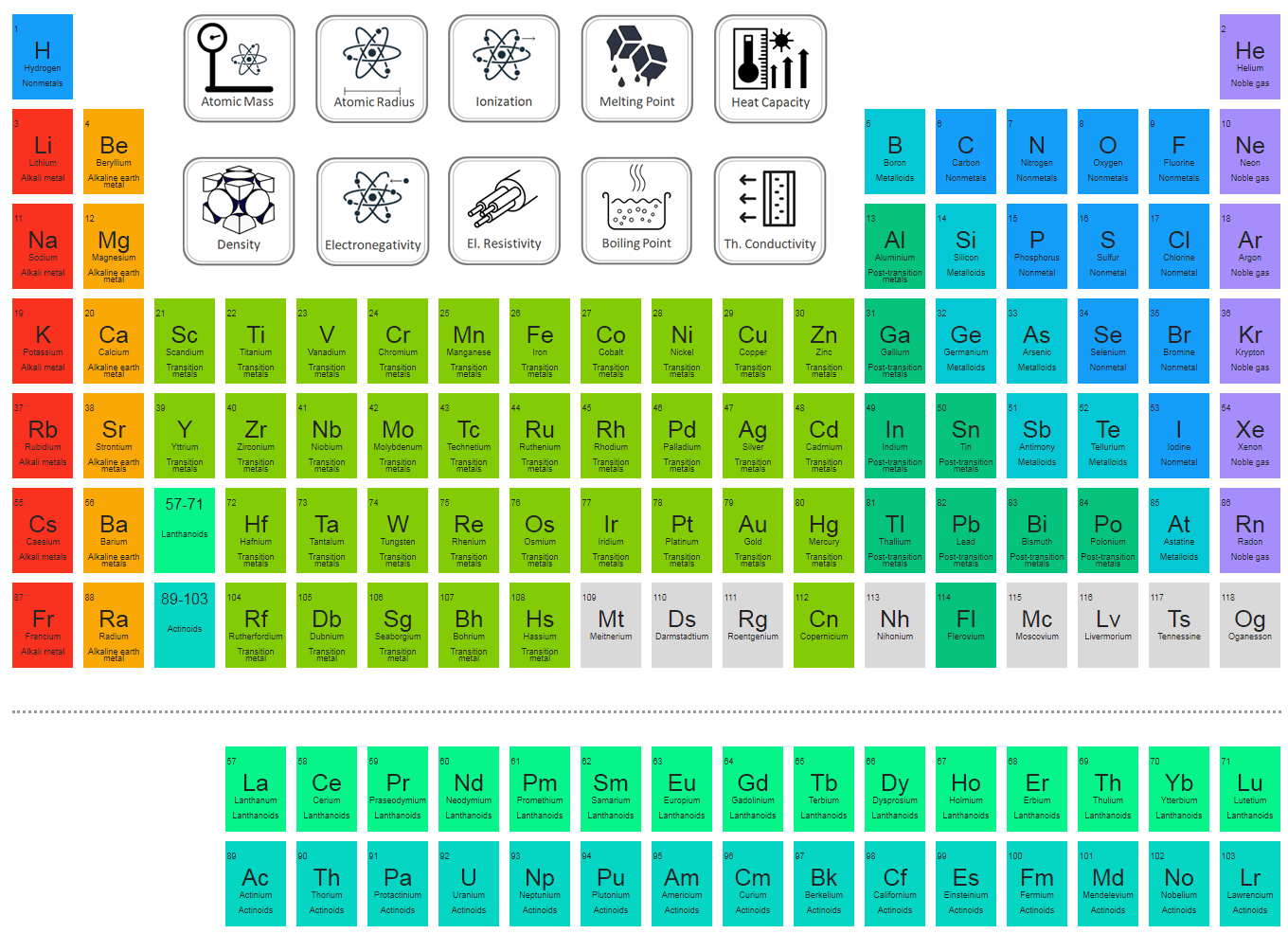

And where B is the net binding energy of a nucleus. Molecular mass (molecular weight) is the mass of one molecule of a substance and is expressed in the unified atomic mass units (u). m ( A, Z) Z ( m p + m e) + ( A Z) m n B / c 2, where subscripts m p, e and n mean proton, electron and the neutron masses, respectively. Weight: Atomic mass of 1.008, 14 times lighter than air Let me elaborate: the atomic mass of some nucleus Z A X N is defined as. Periodic table: element number 1, simplest element on Earth


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
